How the Mediterranean Diet Can Help You Live Longer

Longevity has become a genuine quest in today’s health-focused society. Many seek the secret to extending our lifespans and maintaining the quality of life as we age. Among the numerous dietary options out there, one has consistently gained recognition and respect – the Mediterranean Diet. This diet, rooted in the culinary traditions of the Mediterranean region, isn’t merely about food; it’s a lifestyle. But how can the Mediterranean Diet help you live longer? Let’s delve into the heart of this question.
This diet does not only promote weight management, but research reveals a compelling link between adopting a Mediterranean lifestyle and the promise of healthy longevity. The diet is a rich tapestry of plant-based foods, seafood, olive oil benefits, and even a place for moderate wine consumption. Stay with us as we dive into the Mediterranean Diet’s depths, discovering its components, understanding its science, and sharing stories of people who’ve successfully embraced this lifestyle.
What is the Mediterranean diet?
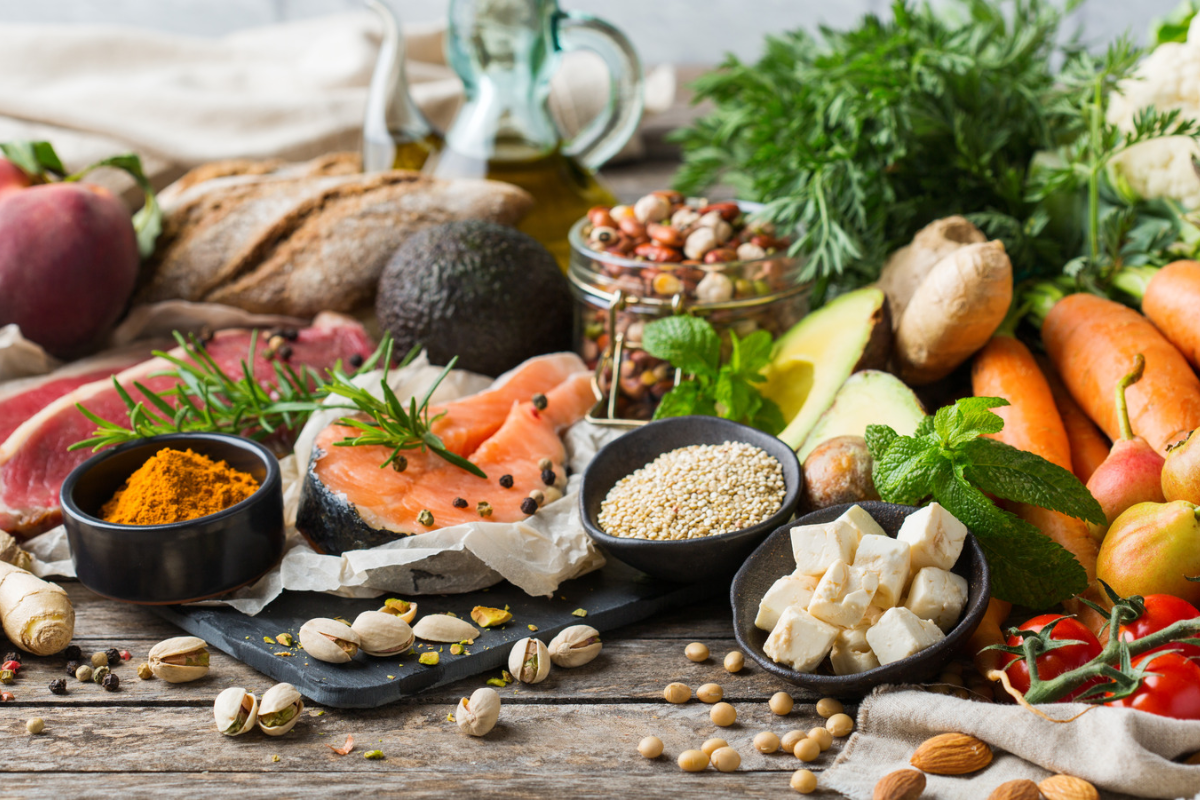
The Mediterranean diet is a dietary pattern inspired by the traditional eating habits of people living in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, and Spain. It is not a strict set of rules but rather a flexible and balanced approach to eating. The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of plant-based foods, whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables.
It includes moderate amounts of fish, poultry, dairy products, and eggs, while red meat and sweets are limited. The diet is also characterized by the use of olive oil as the primary source of fat and the consumption of moderate amounts of wine with meals. It is often associated with the enjoyment of meals with family and friends and an active lifestyle.
Can the Mediterranean diet help you live longer?
Research suggests that following the Mediterranean diet can indeed contribute to a longer and healthier life. Several factors contribute to its positive impact on lifespan. Firstly, the diet is rich in nutrients, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, which can help protect against cellular damage and promote overall health.
The Mediterranean diet includes a variety of foods that have anti-inflammatory effects. Chronic inflammation is a contributing factor to the development of many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. By reducing inflammation, the Mediterranean diet may lower the risk of these conditions. These health improvements, along with the diet’s emphasis on nutrient-dense and anti-inflammatory foods, contribute to enhanced longevity.

A study has shown the diet’s effectiveness in reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases which are major contributors to mortality. The diet includes healthy fats, such as monounsaturated fats found in olive oil and omega-3 fatty acids in fish, which can help improve heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Moreover, the Mediterranean diet’s positive impact extends beyond physical health. It has been linked to improved mental well-being, better sleep quality, and a reduced risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. The combination of wholesome ingredients, antioxidant-rich foods, and healthy fats in the diet appears to support overall brain health.
What makes the Mediterranean diet beneficial to your health?
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by several key components that contribute to its health benefits:
- Abundance of fruits and vegetables: The Mediterranean diet encourages a high intake of colorful, nutrient-rich fruits and vegetables. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber, promoting overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Whole grains: Whole grains like whole wheat, oats, brown rice, and whole-grain bread are staples in the Mediterranean diet. They are a good source of fiber, B vitamins, and minerals, and have been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and improved weight management.
- Legumes and nuts: Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are a primary source of protein in the Mediterranean diet. They are also rich in fiber, minerals, and antioxidants. Nuts, particularly almonds, walnuts, and pistachios, are consumed in moderation and provide healthy fats, fiber, and various nutrients.
- Healthy fats: Olive oil is the principal source of fat in the Mediterranean diet and is used as a primary cooking oil and dressing. It is rich in monounsaturated fats and contains antioxidants. Consuming olive oil has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and improved lipid profiles. Fatty fish, such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel, are also consumed regularly as sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory effects and promote heart health.
- Moderate dairy products: Dairy products like yogurt and cheese, preferably from sources like goat or sheep milk, are consumed in moderate amounts in the Mediterranean diet. They provide calcium, protein, and probiotics.
- Red meat and processed foods are limited: Red meat, processed meats, and processed foods high in unhealthy fats, sodium, and additives are limited in the Mediterranean diet. Instead, lean sources of protein like fish and poultry are favored.
How can individuals incorporate the Mediterranean diet into their daily lives?
Incorporating the Mediterranean diet into daily life can be done gradually and with simple adjustments. Here are some practical tips:
- Increase plant-based food intake: Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts in your meals and snacks. Aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables per day.
- Use olive oil: Replace butter or other cooking oils with olive oil in your recipes and for salad dressings. Opt for extra virgin olive oil for its higher antioxidant content.
- Include fatty fish: Aim to include fatty fish like salmon, sardines, or mackerel in your diet at least twice a week for their omega-3 fatty acids.
- Limit red meat: Reduce the consumption of red meat and processed meats. Instead, opt for lean sources of protein like poultry, fish, legumes, or tofu.
- Choose whole grains: Replace refined grains with whole grains like whole wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, and oats.
- Enjoy fruits and nuts as snacks: Instead of processed snacks, reach for fresh fruits, dried fruits, or a handful of nuts as a healthy snack option.
- Flavor with herbs and spices: Use herbs and spices to add flavor to your dishes instead of relying on excessive salt or unhealthy sauces.
- Moderate wine consumption: If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation and with meals. For those who don’t drink, it’s not necessary to start for the sake of the diet’s principles.
- Share meals with others: The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the social aspect of meals. Enjoy meals with family or friends, and take time to savor and enjoy your food.
- Stay physically active: Incorporate regular physical activity into your daily routine to complement the Mediterranean diet and promote overall health.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Got more questions about how the Mediterranean diet can help you live longer? Check out some commonly asked questions about this topic below.
Is the Mediterranean diet suitable for people with food allergies or intolerances?
Yes, the Mediterranean diet can be adapted to accommodate food allergies or intolerances. Many core components of the diet, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and healthy fats, are generally well-tolerated. Substitutions can be made for specific allergens, such as choosing gluten-free grains or dairy alternatives. Individual needs should be considered, but the diverse range of foods in the Mediterranean diet allows for flexibility.
How the Mediterranean diet can help you live longer?
The Mediterranean diet provides a balanced approach to nutrition that supports healthy aging. It is rich in essential nutrients, antioxidants, and healthy fats, which can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases common in older adults. The emphasis on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and lean proteins contributes to muscle, bone, and cognitive health. Additionally, the social aspect of shared meals promotes overall well-being. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is advised to meet specific nutritional needs.
Can the Mediterranean diet be followed on a budget?
Yes, the Mediterranean diet can be followed without breaking the bank. While some traditional ingredients may be more expensive, the core components are affordable. Emphasizing cost-effective options like fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and plant-based proteins helps save money. Using canned or frozen produce, buying in bulk, and choosing seasonal ingredients further reduces costs. Minimizing processed foods and making smart meal-planning choices contribute to a budget-friendly Mediterranean diet. Enjoying the health benefits is possible with mindful choices and cost-conscious approaches.
Final Word
We’ve embarked on a fascinating exploration of the Mediterranean Diet, uncovering its potential in extending our lives. Isn’t it intriguing how something as simple and enjoyable as our daily meals can hold such a profound impact on our lifespan? As we delve into the components of this lifestyle, we recognize its holistic approach – a balance of nutritious foods, physical activity, and an appreciation for the joy of eating.
If you’ve found these insights valuable, don’t keep it to yourself. Share this article with a friend who might also be curious about how the Mediterranean Diet can enhance their life expectancy. And for more tips on healthy living and longevity, make sure to delve deeper into our blog. Here’s to a healthier, longer life!